Introduction – Networking enhances communication reliability and convenience by connecting network devices through various means, such as wired or wireless connections. Network Topologies define the connection types that link computers and other networking devices, facilitating their communication with each other. Consequently, Network Topologies play a crucial role. The concept of Network Topology forms the very backbone of communication systems, ensuring seamless data transfer and connectivity.
Definition:
Network Topology refers to the arrangement of various elements in a computer network. Understanding Network Topology is crucial for designing efficient, robust, and scalable networks. Therefore, let’s explore the most common Network Topologies, along with their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Each topology have advantages and on the other hand dis-advantages too.
Types of Network Topologies
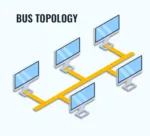
Bus Topology: All the Networking devices are connection with Single Central Cable, known as Bus. Data sent from one device travels along the bus until it reaches its destination.
Advantages: Easy to install and understand. Requires less cable compared to other topologies.
Dis-Advantages: Data collisions can occur, leading to network inefficiencies. The entire network is dependent on a single cable, making it less scalable.
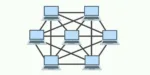
Mesh Topology: In a mesh topology, each device connects to every other device. This can form a full mesh, where all devices interconnect, or a partial mesh, where only some devices interconnect
Advantages: Multiple paths exist for data, ensuring network reliability and robustness. Easy to expand without disrupting the existing network.
Dis-Advantages: Requires complex configurations and management. High cabling cost due to extensive connections.
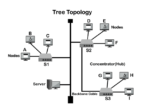
Tree Topology: Tree topology is a hybrid topology that combines characteristics of star and bus topologies. Devices arrange themselves in a hierarchical manner, connecting groups of star-configured networks to a linear bus backbone.
Advantages: Facilitates efficient data management and organization. Easily expandable by adding new branches.
Dis-Advantages: If the backbone line fails, the entire network segment goes down. It can be complex to configure and manage.
Most Commonly Used Topologies
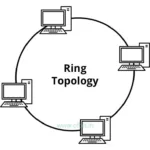
Ring Topology: Each device connects to exactly two neighbours in a circular fashion, forming a ring topology. Data travels in one direction (or both directions in a bidirectional ring) until it reaches its destination.
Advantages: All devices have equal access to the network. Faults are easy to locate.
Dis-Advantages: A single point of failure disrupts the entire network when one device or connection fails. Data must travel through multiple devices, which can introduce latency.
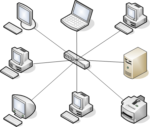
Star Topology: In a star topology, all devices connect to a central hub or switch. The hub repeats data flow.
Advantages: High Performance: Devices send data directly to the intended device, reducing collisions. Adding or removing devices is straightforward.
Dis-Advantages: The entire network depends on the central hub. If the hub fails, the network goes down. It requires more cables compared to bus and ring topologies.
However, all of this advantages and dis-advantages, Star Topology is used widely.
Made with ♥ with 10% help of Microsoft Copilot.