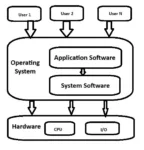
Hi everyone, As you already knew that there are two types of Software, one is application software and other is system software. Operating System is the types of System Software.
Application Software: The software that is used for a specific task is known as Application Software such as WhatsApp, Facebook, MS Office, Photoshop etc.
System Software: A System software is used to provide interface between the hardware and user. With the use of system software you can use hardware for example, one can use PC with a Operating System, One can use printer with its printer driver, etc. Similarly, Operating System is a type of System Software which performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripherals such as disk drives and printers.
Single User and Multi User Operating System
A Single User Operating System is in which only one user can access the computer system at a time. For example, Digital Stopwatch etc. Multi user Operating Systems can be used by a number of users at a time. For example, Windows, MacOS, Linux, UNIX etc.
Batch OS:
In this OS, the computer does not directly interact with the user. Instead, the user writes commands on devices such as a memory card or USB. Subsequently, the computer operator places a batch of jobs on an input device. Afterward, a special program processes and executes each program in the batch. For instance, industrial machines utilize Batch OS.
In this OS, the computer does not directly interact with the user. Instead, the user writes commands on devices such as a memory card or USB. Subsequently, the computer operator places a batch of jobs on an input device. Afterward, a special program processes and executes each program in the batch. For instance, industrial machines utilize Batch OS.
Multi Programming OS:
The operating system picks up a job from memory and begins to execute it. When this job requires an I/O operation, the operating system immediately switches to another job. As a result, both the CPU and the operating system remain constantly busy. Moreover, the number of jobs in memory is always less than the number of jobs present on the disk, which forms the Job Pool. If multiple jobs are ready to run simultaneously, the system selects one through the process of CPU scheduling. However, in a non-multiprogramming system, the CPU occasionally remains idle and does no work. In contrast, a multiprogramming system ensures that the CPU is never idle and continuously processes jobs.
Time Sharing OS:
It is very similar to multi-programming batch systems. In fact, time sharing systems are an extension of multi-programming systems. Time sharing is a technique which enables many people, located at various terminals, to use a particular computer system at the same time. In Time sharing systems the prime focus is on minimizing the response time, while in multi-programming the prime focus is to maximize the CPU usage. The CPU executes multiple jobs by frequently switching between them. The switches happen so rapidly that they maintain seamless processing. Thus, the user can receive an immediate response.
Multi Processor OS:
A Multi-processor system consists of several processors that share a common physical memory. Multi-processor system provides higher computing power and speed. In Multi-processor system all processors operate under single operating system. Multi-Processor OS refers to the use of two or more CPUs within a single computer system. These multiple CPUs are in a close communication sharing the computer bus memory and other peripheral devices.
Network OS:
A Network OS runs on a server and provides the server the capability to manage data, users, groups, security, applications, and other networking functions. The primary purpose of the network OS is to allow shared file and printer access among multiple computers in a network, typically a local area network (LAN), a private network or to other networks. Examples of network OS include Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Microsoft Windows Server 2008, UNIX, Linux, Mac OS X.
Real Time OS:
A real-time system processes data and responds to input within a specific time interval, known as the response time. This method ensures a much shorter response time compared to online processing. Moreover, real-time systems meet rigid time requirements for processor operations or data flow. Additionally, these systems serve as control devices in dedicated applications. A real-time operating system must have well-defined, fixed time constraints, otherwise the system will fail. For example, Scientific experiments, medical imaging systems, industrial control systems, weapon systems, robots, air traffic control systems, etc.
Mobile OS:
A Mobile OS is an OS that helps to run other application software on mobile devices. It is the same kind of software as the famous computer operating systems like Linux and Windows, but now they are light and simple to some extent. For Example: iOS, Android, Windows Mobile.
Read About What is Android?
Made with ♥ with the 10% help of Google Gemini


